Highlights and Lessons learnt from the Spanish Pilot
The Pilot 2 in Spain, carried out by VEOLIA, has achieved significant progress in optimizing energy efficiency and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
This pilot is divided into three use cases: UC3, UC4, and UC5, each with specific objectives. For the UC3 and UC5 the demonstrator is the District Heating Cooling (DHC) network of the Reina Sofía Hospital in the city of Córdoba, and for the UC4 a residential building in Burgos.
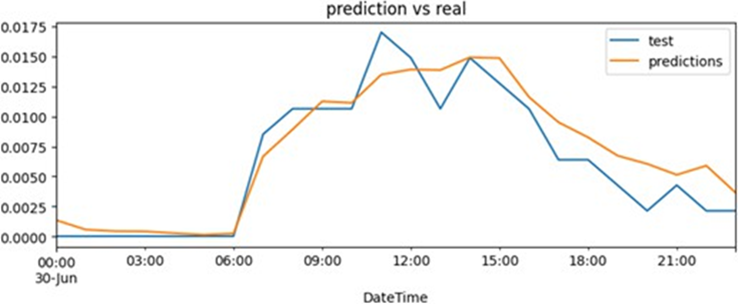
UC3 aims to reduce energy consumption in the District Heating Network (DHN) by predicting energy demand and optimizing DHN operation. To achieve this, artificial intelligence (AI)-based energy demand prediction models have been developed. These models allow adjusting energy production to demand, resulting in lower energy consumption and a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
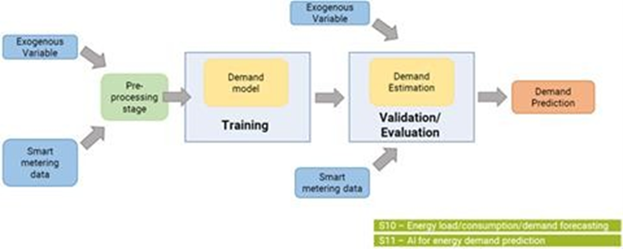
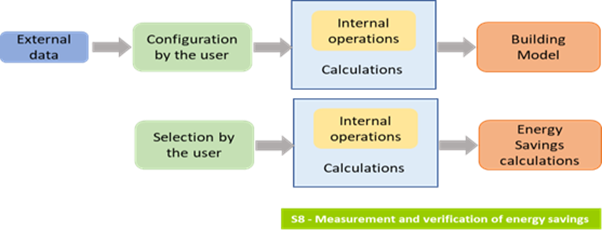
On the other hand, UC4 focuses on increasing confidence in Energy Performance Contracts through an AI-based energy savings verification service. This service uses AI models and algorithms to verify energy savings obtained in these contracts, ensuring their compliance and effectiveness.
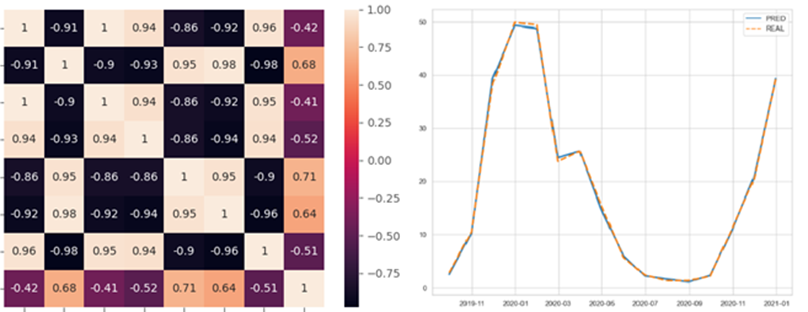
UC5 aims to optimize the production combination in multi-energy systems using AI tools. Achieving this requires accurate energy demand predictions supported by precise weather forecasts. These predictions enable informed decisions about energy production, leading to greater efficiency and energy savings.
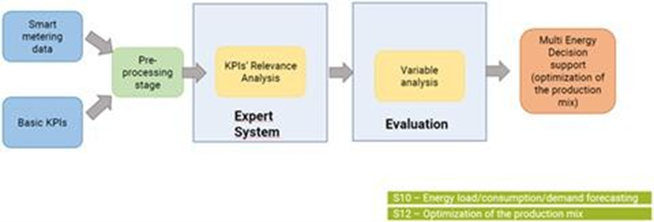
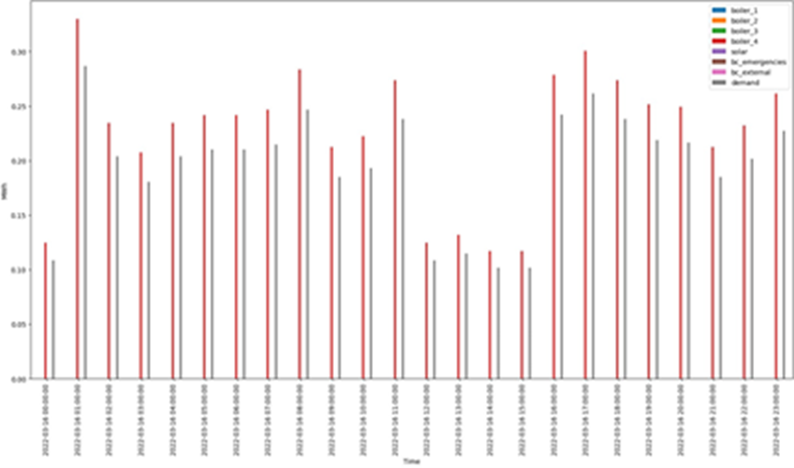
In terms of results, prediction models and services have been developed for each use case. In UC3, two models and related services related to heat and cold demand prediction have been developed. In UC4, an energy savings verification service has been developed. And in UC5, optimization tools for the production combination in multi-energy systems have been developed.
These advances in Pilot 2 in Spain demonstrate the potential of artificial intelligence to improve energy efficiency, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and increase confidence in energy performance contracts. These results are a significant step toward a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.

